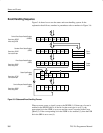
Status and Events
TLS 216 Programmer Manual
3–7
When output is sent to the Output Queue, the MAV bit in the SBR is set to
one (5).
When a bit in the SBR is set to one and the corresponding bit in the SRER is
enabled (6), the MSS bit in the SBR is set to one and a service request is
generated (7).
Synchronization Methods
Although most GPIB commands are completed almost immediately after being
received by the logic scope, some commands initiate processes requiring
additional time. For example, once a HARDCOPY START command is
executed it may be a few seconds before the hardcopy operation is complete.
Rather than remain idle while the operation is in process, the logic scope will
continue processing other commands. This means that some operations will not
be completed in the order that they were sent.
Sometimes the result of an operation depends on the result of an earlier operation
(the first operation must be completed before the next one is initiated). The status
and event reporting system of the logic scope provides this capability.
For example, a typical application might involve acquiring a single-sequence
waveform then taking a measurement on the acquired waveform. You could use
the following command sequence to do this:
/* Set up single-sequence acquisition */
SELECT:GROUP1 ON
GROUP1:FIRST 1
/* Take amplitude measurement on acquired data */
MEASUREMENT:IMMED:VALUE?
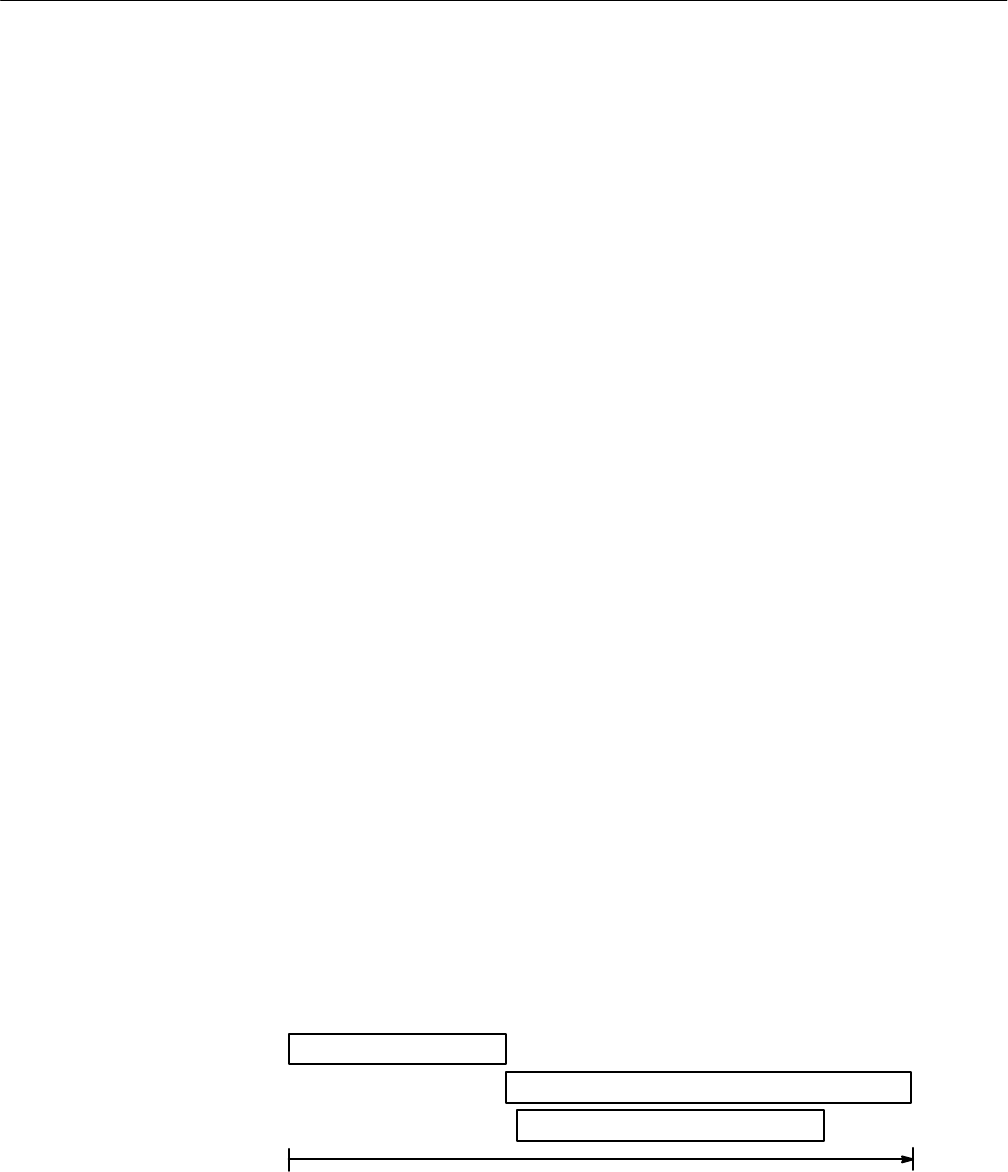
The acquisition of the waveform requires extended processing time. It may not
finish before the logic scope takes an amplitude measurement (See Figure 3–7).
This can result in an incorrect amplitude value.
MEASUREMENT:IMMED:VALUE?
Processing Time
Acquiring Waveform Data
ACQUIRE:STATE ON
Figure 3–7: Command Processing Without Using Synchronization