Command Syntax
2–2
TLS 216 Programmer Manual
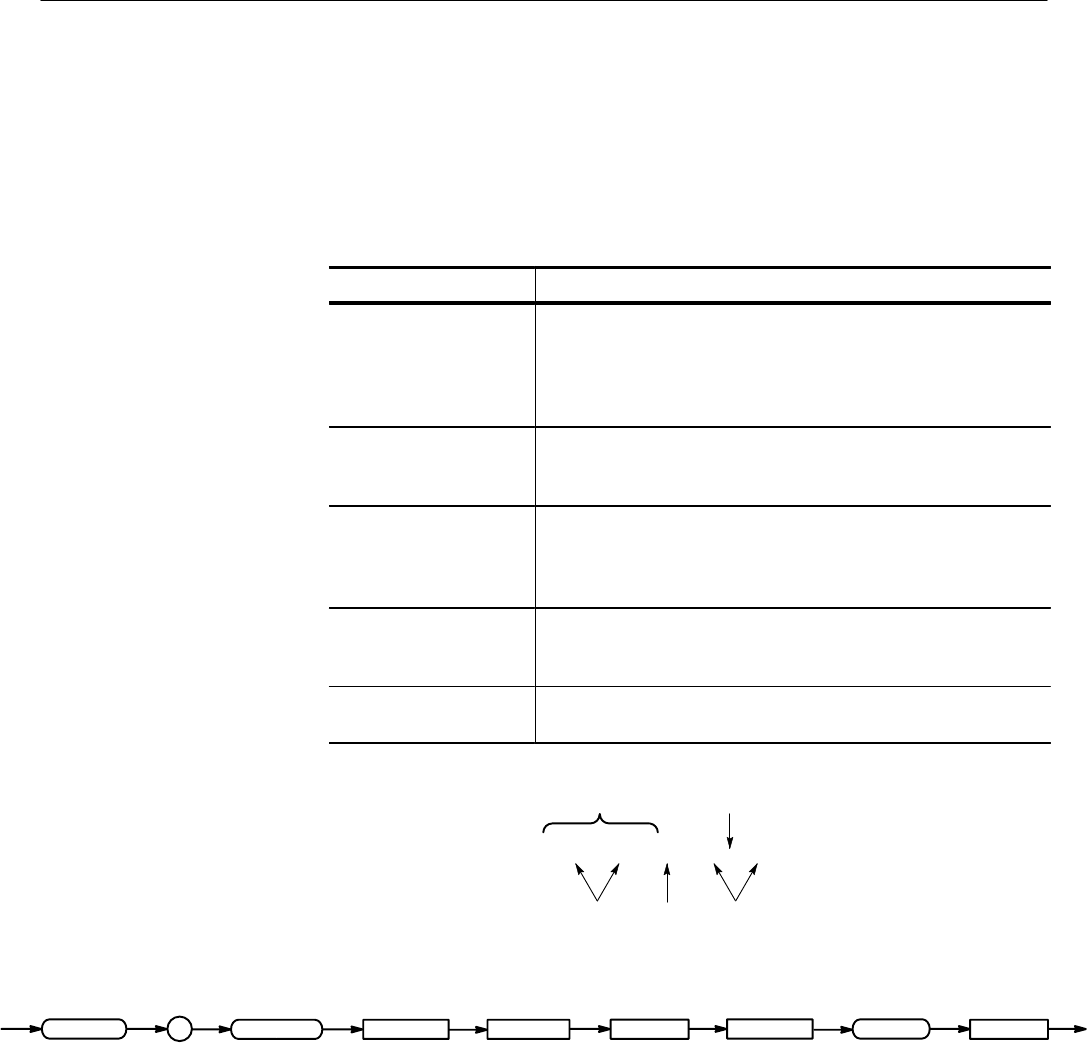
A command message is a command or query name followed by any information
the logic scope needs to execute the command or query. Command messages
may contain five element types, defined in Table 2–2 and shown in the example
in Figure 2–1.
Table 2–2: Command Message Elements
Symbol Meaning
<Header> The basic command name. If the header ends with a question
mark, the command is a query. The header may begin with a colon
(:) character. If the command is concatenated with other
commands, the beginning colon is required. Never use the
beginning colon with command headers beginning with a star (*).
<Mnemonic> A header sub-function. Some command headers have only one
mnemonic. If a command header has multiple mnemonics, a colon
(:) character always separates them from each other.
<Argument> A quantity, quality, restriction, or limit associated with the header.
Some commands have no argument while others have multiple
arguments. A <Space> separates arguments from the header. A
<Comma> separates arguments from each other.
<Comma> A single comma between arguments of multiple-argument
commands. It may optionally have white space characters before
and after the comma.
<Space> A white space character between command header and argument.
It may optionally consist of multiple white space characters.
Comma
SAVe:GROUP GRP1,REF3
Header
Mnemonics ArgumentsSpace
<GRP>
SAVe :
GROUP
REF
<x><Space>
<Comma>
Command Parts
Syntax Diagram
<x>
Figure 2–1: Command Message Elements