VIX IM MICROSTEPPER INDEXER DRIVE USER GUIDE
60
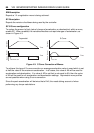
EI Description
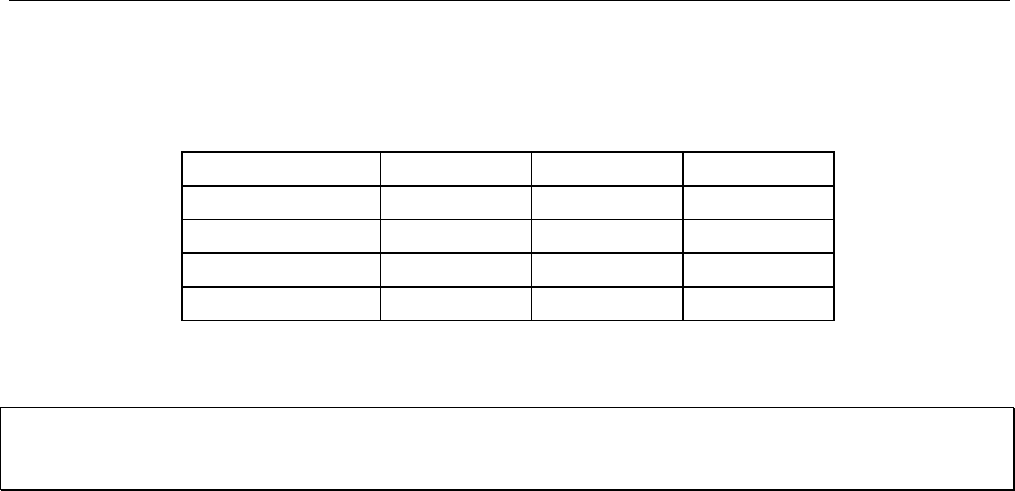
System parameter EI, controls encoder inputs (connector X4) as defined in Table 4-4.
X4 EI=0 EI=1 EI=2
12 STEP+ CW+ A+
7 STEP- CW- A-
13 DIR+ CCW+ B+
8 DIR- CCW- B-
Table 4-4. Encoder Input Configuration
CAUTION
De-energise the drive before changing EI and EO.
EQ Description
Echo queuing (EQ) is a system variable that can be useful for multi-axis control programs
where you need to send and receive messages from individual drives controlled from a PC.
The variable controls the way messages are echoed and its use prevents corruption of
commands by system response messages. In a normal multi-axis system, commands from
the main controller are, in turn, echoed from drive to drive throughout the system and can be
finally returned to the main controller. If a command is transmitted whilst a drive is supplying
a response the two messages will interact, effectively destroying one another. Setting EQ to
mode 1 prevents a drive from issuing a response until it receives a carriage return, thereby
delaying its response until it finishes receiving. This stops the corruption of messages, which
can now be read back in a complete form.
EQ can only be used with a report or write command, as follows:
R(EQ) reads the current setting of the system variable.
W(EQ, 0 - 2) sets the EQ system variable to operate in mode 0, 1 or 2.
Mode 0 sets the standard operating mode where characters are echoed as they are sent.
Mode 1 does not allow any characters to be echoed until a carriage return is sent. This
prevents complete messages from being split if a data collision occurs.
Mode 2 allows only the response from a command to be sent, not the command itself. This
minimises the amount of data being transferred and therefore helps to reduce the chance of
a transmit buffer overflow.
Note: The set address command (#) will be echoed irrespective of the state of the echo
queuing variable.