Chapter 3: Graph & Table Application 112
3-6 Analyzing a Function Used to Draw a Graph
Your ClassPad includes a G-Solve feature that lets you perform a variety of different analytical processes on an
existing graph.
What You Can Do Using the G-Solve Menu Commands
While there is a graph on the Graph window, you can use a [G-Solve] menu command to obtain the following
information.
•
x-coordinate for a given y-coordinate .................................................Analysis - G-Solve - x-Cal/y-Cal - x-Cal
•
y-coordinate for a given x-coordinate .................................................Analysis - G-Solve - x-Cal/y-Cal - y-Cal
• Root (the
x-intercept) .................................................................................... Analysis - G-Solve - Root or Y
• Minimum value ................................................................................................Analysis - G-Solve - Min or I
• Maximum value ..............................................................................................Analysis - G-Solve - Max or U
• Minimum value in the range displayed on the Graph window ................................. Analysis - G-Solve -
f Min
• Maximum value in the range displayed on the Graph window ............................... Analysis - G-Solve - f Max
•
y-intercept ......................................................................................................Analysis - G-Solve - y-Intercept
• Point of intersection for two graphs .............................................................. Analysis - G-Solve - Intersection
• Integration value for a specified range ........................................................ Analysis - G-Solve - Integral - ∫
dx
• Integration value between the two or more of the graph’s roots .............. Analysis - G-Solve - Integral - Root
• Integration value between the two or
more intersections of two graphs ............................................. Analysis - G-Solve - Integral - Intersection
• Point of inflection ...............................................................................................Analysis - G-Solve - Inflection
• Distance between two points ............................................................................Analysis - G-Solve - Distance
• Volume of a solid of revolution ......................................................................... Analysis - G-Solve - π ∫
f(x)
2
dx
Tip:
See “Graph Types and Executable Functions” (page 266) for information about graph types and executable G-Solve
functions.
Using G-Solve Menu Commands
When multiple solutions are obtained by a G-Solve command, only one solution is displayed at a time. For
example, executing [Analysis] - [G-Solve] - [Root] for a cubic function that has two roots will display only one
root at a time. In a case such as this, use the left and right cursor keys (or tap the left and right graph controller
arrows) to cycle between the available solutions.
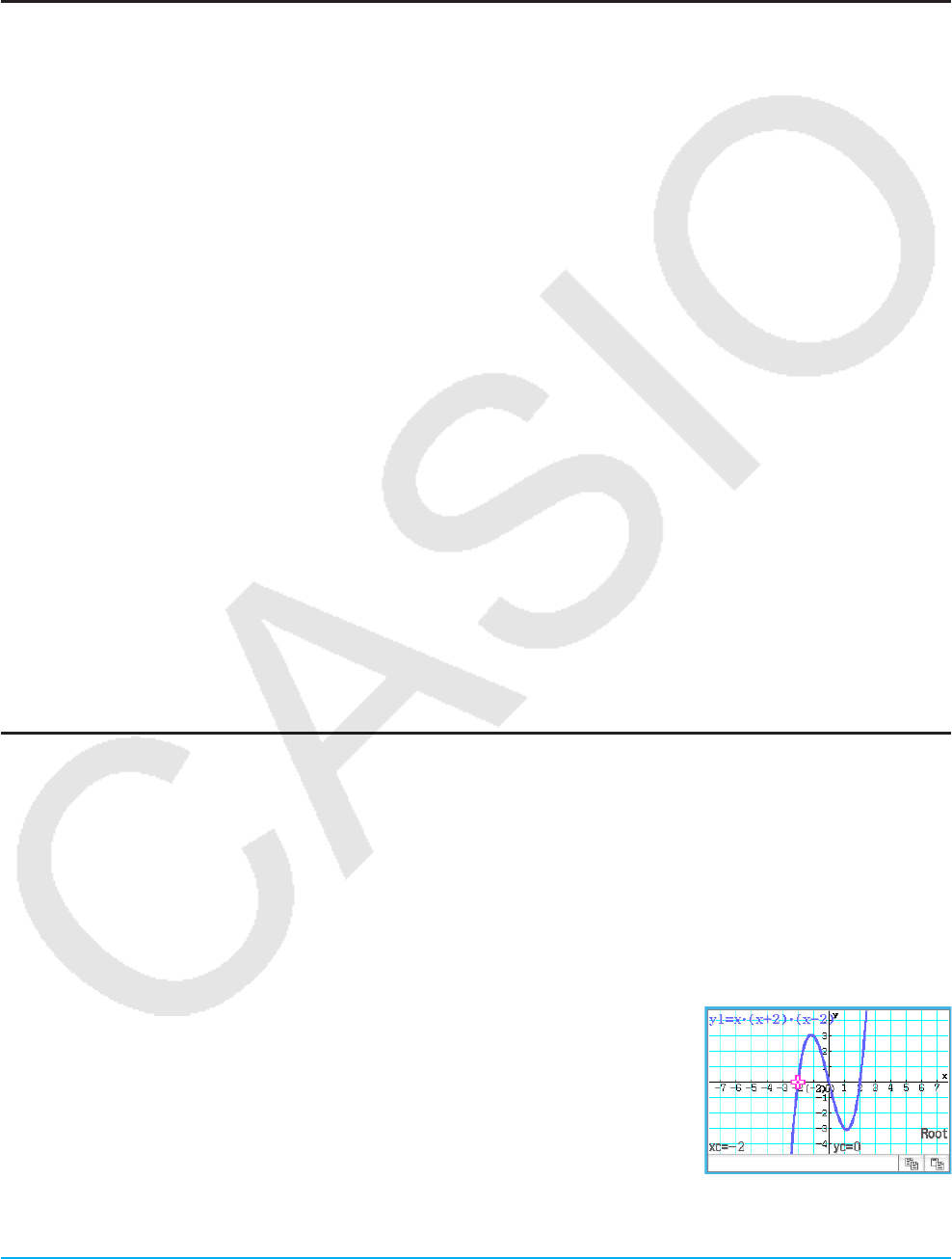
u To obtain the root of a function
1. On the Graph Editor window, input and store a function, and then tap $ to graph it.
• Here, input
y = x(x + 2)(x – 2) into line y1.
2. Tap [Analysis], [G-Solve], and then [Root], or tap Y.
• This displays “Root” on the Graph window, and locates a pointer at the first
solution of the root (root for smallest value of
x). The x- and y-coordinates
at the current pointer location are also shown on the Graph window.
