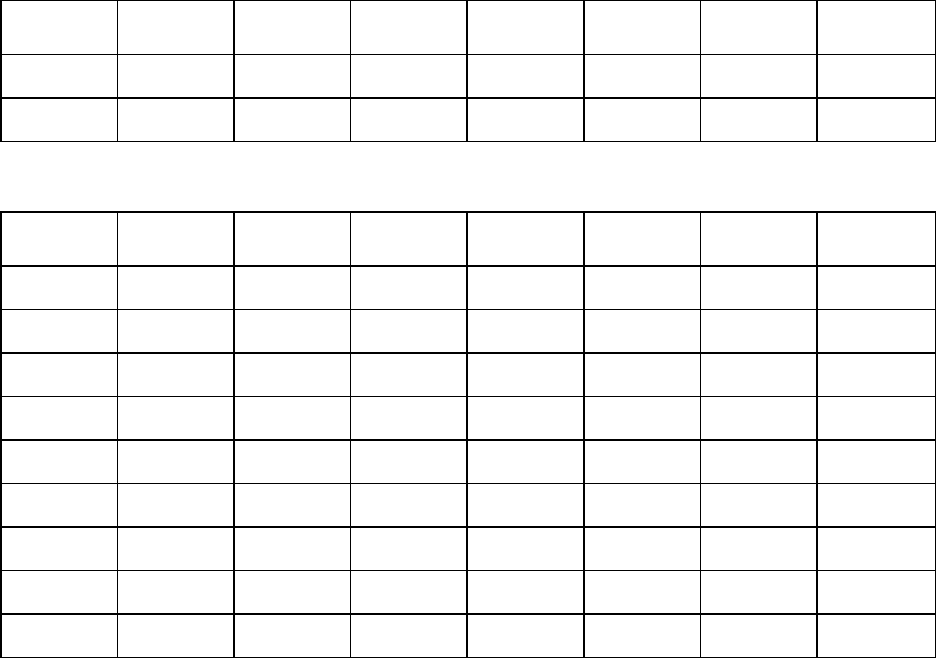
70
Age / Years
Very low Low Fair Moderate Good Very good Elite
55-59 < 22 22-26 27-30 31-34 35-39 40-43 > 43
60-65 < 21 21-24 25-28 29-32 33-36 37-40 > 40
Women
Age / Years
Very low Low Fair Moderate Good Very good Elite
20-24 < 27 27-31 32-36 37-41 42-46 47-51 > 51
25-29 < 26 26-30 31-35 36-40 41-44 45-49 > 49
30-34 < 25 25-29 30-33 34-37 38-42 43-46 > 46
35-39 < 24 24-27 28-31 32-35 36-40 41-44 > 44
40-44 < 22 22-25 26-29 30-33 34-37 38-41 > 41
45-49 < 21 21-23 24-27 28-31 32-35 36-38 > 38
50-54 < 19 19-22 23-25 26-29 30-32 33-36 > 36
55-59 < 18 18-20 21-23 24-27 28-30 31-33 > 33
60-65 < 16 16-18 19-21 22-24 25-27 28-30 > 30
The classification is based on a literature review of 62 studies where VO
2max
was measured directly in
healthy adult subjects in the USA, Canada and 7 European countries. Reference: Shvartz E, Reibold RC.
Aerobic fitness norms for males and females aged 6 to 75 years: a review. Aviat Space Environ Med; 61:3-11,
1990.
ORTHOSTATIC TEST
Orthostatic test is a generally used tool for monitoring the balance between training and recovery. It is based
on the training-induced changes in the function of your autonomic nervous system. Orthostatic test results are
affected by several external factors, such as mental stress, sleep, latent illness, environmental changes
(temperature, altitude), and others. Long term follow-up helps you to optimize your training and prevent
overtraining.
Orthostatic test is based on the measurement of heart rate and heart rate variability. Changes in heart rate and
heart rate variability reflect the changes in autonomic regulation of the cardiovascular system. During the test
HRrest, HRstand and HRpeak are measured. Heart rate and heart rate variability measured during orthostatic
test are good indicators of disturbances in the autonomic nervous system, for example fatigue or overtraining.
However, heart rate responses to fatigue and overtraining are always individual, and require longer term
follow-up.


















