40 | C1508M (02/01)
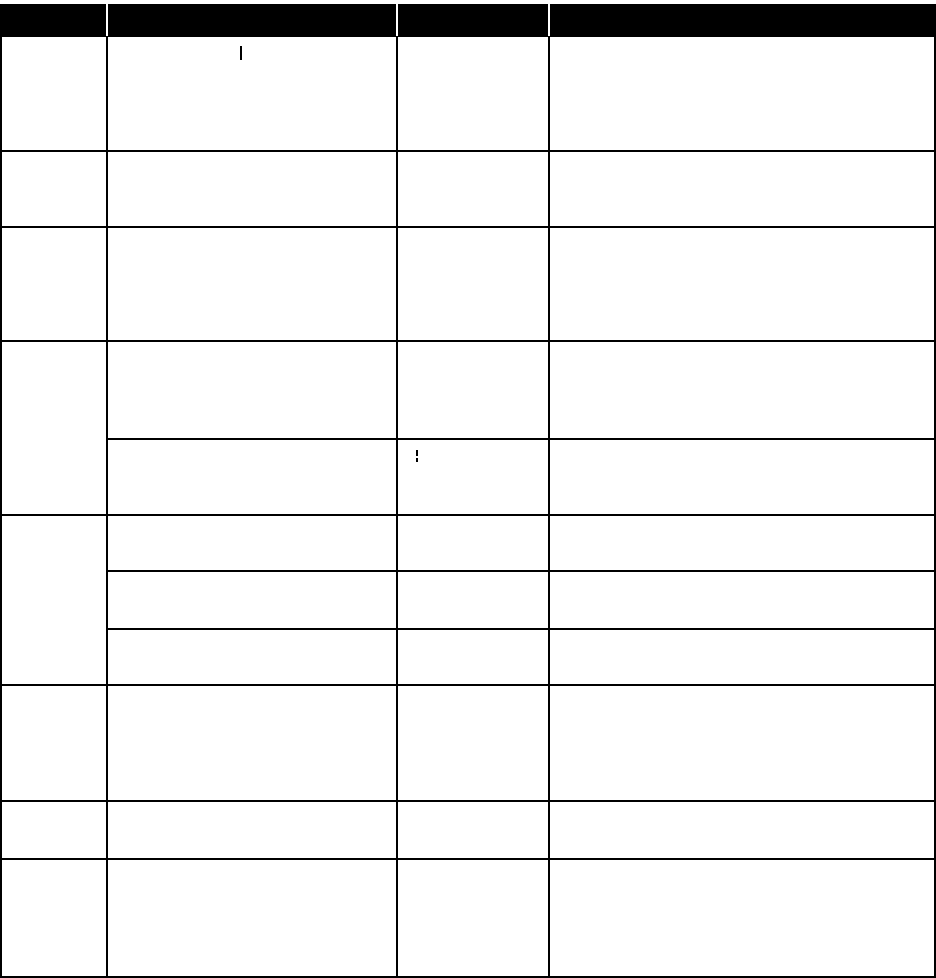
MORE C:\>DIR C:\DOS MORE
PATH PATH=C:\;C:\dos;C:\windows
RENAME or C:\>RENAME C:\9740\TEST.*
REN TESTALL.*
C:\>REN C:\9740\TEST.* TESTALL.*
TYPE C:\>TYPE C:\9740\TEST.MON
C:\>TYPE C:\9740\TEST.ALM MORE
MORE
UNDELETE C:\>UNDELETE C:\9740\TEST.BAT
C:\>UNDELETE C:\9740\ /LIST /LIST
C:\>UNDELETE C:\9740\ /ALL /ALL
RMDIR or C:\>RMDIR NETWORK
RD C:\>RD NETWORK
VER C:\>VER
TREE C:\> TREE
Displays one screen of information at a time. Can
also be used with the TYPE command when
viewing a long text file. The symbol is called a
redirection operator. On the keyboard, it is located
above the backslash \ symbol.
Indicates which directories DOS should search for
executables. By default, DOS searches just the
current directory.
Changes the name of the file or files you specify.
Specify the name and location of the file or files to
be changed. The last part of the command
specifies the new name. You cannot specify a new
drive or path.
Displays the contents of the text file you specify.
You must specify a directory path if the location of
the file is in a directory other than the one you are
in.
Here the MORE redirection operator is used to
enable us to view the alarm file (usually quite
long), one page at a time.
Restores files that were previously deleted using
the DEL command.
Lists the deleted files can be recovered, but does
not recover any files.
Recovers deleted files without prompting for
confirmation on each file.
Deletes or removes a directory. Before the
directory can be deleted, it must contain no files
or other subdirectories. The directory must be
completely empty except for the “ . ” and “ . . ”
symbols.
Displays the current version of DOS on your
machine.
Displays the directory structure of all the
directories on your hard drive if it is issued while
in the root directory; otherwise, it will display only
the subdirectories of the directory you are
currently in.
Table D
DOS Command Reference Directory (Continued)
COMMAND EXAMPLE(S) SWITCHES COMMENTS
