4
Operation Guide 3173 3246
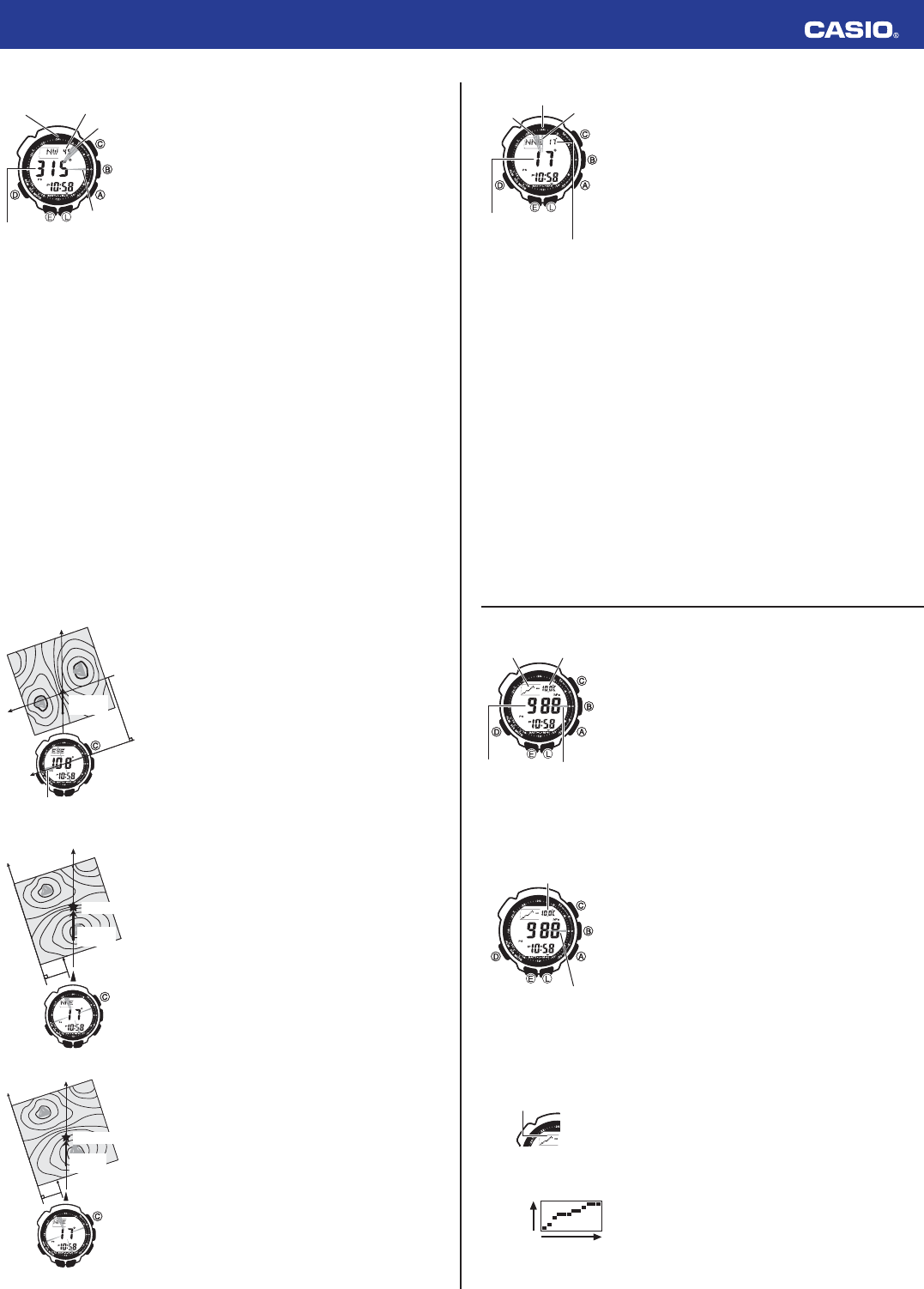
Bearing Memory
Bearing Memory lets you store a direction reading and display that
reading as you take subsequent digital compass measurements. The
Bearing Memory screen displays the direction angle for the stored
direction, along with an indicator on the display that also indicates the
stored direction.
When you take digital compass measurements while the Bearing Memory
screen is on the display, the direction angle of the current digital compass
measurement (as read from the 12 o'clock position of the watch) and the
currently stored Bearing Memory direction information will both be
displayed.
To store a direction angle reading in Bearing Memory
1. Press
C
to start a digital compass measurement operation.
• If a bearing memory direction angle value is already displayed,
it means that the bearing memory screen is displayed. If this
happens, press
E
to clear the value currently in Bearing Memory
and exit the bearing memory screen.
2. During the 20 seconds that digital compass measurement is in
progress, press
E
to store the current direction angle reading in
Bearing Memory.
• The Bearing Memory direction angle fl ashes for about one second
as it is stored in Bearing Memory. After that, the Bearing Memory
screen (which shows the bearing memory direction angle) will
appear, and a 20-second direction reading operation will start.
• While the Bearing Memory screen is displayed, you can press
C
to start a new 20-second
direction reading operation, which displays the direction angle for the direction that the 12 o’clock
position of the watch is pointed. The direction angle of the current readings will disappear from the
display after the direction reading operation is complete.
• During the fi rst 20 seconds after you display the Bearing Memory screen or during the 20-second
direction reading operation while the Bearing Memory screen is on the display, the direction
stored in memory is indicated by a Bearing Memory pointer.
• Pressing
E
while the Bearing Memory screen is displayed will clear the direction angle currently
in Bearing Memory and start a 20-second direction reading operation.
Using the Digital Compass While Mountain Climbing or Hiking
This section provides three practical applications for using the watch’s built-in digital compass.
• Setting a map and fi nding your current location
Having an idea of your current location is important when mountain climbing or hiking. To do this, you
need to “set the map”, which means to align the map so the directions indicated on it are aligned with
the actual directions of your location. Basically what you are doing is aligning north on the map with
north as indicated by the watch.
• Finding the bearing to an objective
• Determining the direction angle to an objective on a map and heading in that direction
To set a map and fi nd your current location
1. With the watch on your wrist, position it so the face is horizontal.
2. While in the Timekeeping Mode or in any of the sensor modes, press
C
to take a compass reading.
• The reading will appear on the display after about two seconds.
3. Rotate the map without moving the watch so the northerly direction
indicated on the map matches north as indicated by the watch.
• If the watch is confi gured to indicate magnetic north, align the
map’s magnetic north with the watch indication. If the watch has
been confi gured with a declination to correct to true north, align
the map’s true north with the watch indication. For details, see
“Calibrating the Bearing Sensor”.
• This will position the map in accordance with your current location.
4. Determine your location as you check the geographic contours around
you.
To fi nd the bearing to an objective
1. Set the map so its northerly indication is aligned with north as indicated
by the watch, and determine your current location.
• See “To set a map and fi nd your current location” for information
about how to perform the above step.
2. Set the map so the direction you want to travel on the map is pointed
straight in front of you.
3. With the watch on your wrist, position it so the face is horizontal.
4. While in the Timekeeping Mode or in any of the sensor modes, press
C
to take a compass reading.
• The reading will appear on the display after about two seconds.
5. Still holding the map in front of you, turn your body until north as
indicated by the watch and the northerly direction on the map are
aligned.
• This will position the map in accordance with your current location,
so the bearing to your objective is straight ahead of you.
To determine the direction angle to an objective on a map and head in that direction
1. Set the map so its northerly indication is aligned with north as indicated
by the watch, and determine your current location.
• See “To set a map and fi nd your current location” for information
about how to perform the above step.
2. As shown in the illustration to the left, change your position so you (and
the 12 o’clock position of the watch) are pointed in the direction of
objective, while keeping the northerly direction indicated on the map
aligned with north as indicated by the watch.
• If you fi nd it diffi cult to perform the above step while keeping
everything aligned, fi rst move into the correct position (12 o’clock
position of the watch pointed at the objective) without worrying
about the orientation of the map. Next, perform step 1 again to set
the map.
12 o’clock
position
Bearing memory
direction angle
North
pointer
Direction angle of
current reading
Bearing Memory
Screen
Bearing
memory
pointer
12 o’clock
position
Bearing memory
direction angle
North
pointer
Direction angle of
current reading
Bearing Memory
Screen
Bearing
memory
pointer
N
N
Current
location
North indicated
on the map
North indicated by
north pointer
N
N
Current
location
North indicated
on the map
North indicated by
north pointer
N
N
Objective
Current
location
12 o’clock
position
N
N
Objective
Current
location
12 o’clock
position
N
N
Objective
Current
location
12 o’clock
position
N
N
Objective
Current
location
12 o’clock
position
3. While in the Timekeeping Mode or in any of the sensor modes, press
C
to take a compass reading.
4. While direction angle readings are in progress, press
E
to record the
currently displayed direction in Bearing Memory.
• The direction angle value and pointer stored in Bearing Memory
will remain on the display for about 20 seconds.
• See “Bearing Memory” for more information.
5. Now you can advance while monitoring the Bearing Memory pointer to
ensure that it remains in the 12 o’clock position.
• To re-display the Bearing Memory direction angle value and
Bearing Memory pointer, press
C
.
• Pressing
E
while the Bearing Memory direction angle value and
Bearing Memory pointer are on the display will clear the Bearing
Memory data you saved in step 3 and save the current direction
reading in Bearing Memory.
Note
• When mountain climbing or hiking, conditions or geographic
contours may make it impossible for you to advance in a straight
line. If this happens, return to step 1 and save a new direction to
the objective.
Digital Compass Precautions
This watch features a built-in magnetic bearing sensor that detects terrestrial magnetism. This means that
north indicated by this watch is magnetic north, which is somewhat different from true polar north. The
magnetic north pole is located in northern Canada, while the magnetic south pole is in southern Australia.
Note that the difference between magnetic north and true north as measured with all magnetic compasses
tends to be greater as one gets closer to either of the magnetic poles. You should also remember that
some maps indicate true north (instead of magnetic north), and so you should make allowances when
using such maps with this watch.
Location
• Taking a direction reading when you are near a source of strong magnetism can cause large errors in
readings. Because of this, you should avoid taking direction readings while in the vicinity of the
following types of objects: permanent magnets (magnetic necklaces, etc.), concentrations of metal
(metal doors, lockers, etc.), high tension wires, aerial wires, household appliances (TVs, personal
computers, washing machines, freezers, etc.).
• Accurate direction readings are impossible while in a train, boat, air plane, etc.
• Accurate readings are also impossible indoors, especially inside ferroconcrete structures. This is
because the metal framework of such structures picks up magnetism from appliances, etc.
Storage
• The precision of the bearing sensor may deteriorate if the watch becomes magnetized. Because of
this, you should store the watch away from magnets or any other sources of strong magnetism,
including: permanent magnets (magnetic necklaces, etc.) and household appliances (TVs, personal
computers, washing machines, freezers, etc.).
• Whenever you suspect that the watch may have become magnetized, perform the procedure under “To
perform bidirectional calibration”.
Barometer/Thermometer
This watch uses a pressure sensor to measure air pressure (barometric pressure) and a temperature
sensor to measure temperature.
To enter and exit the Barometer/Thermometer Mode
1. While in the Timekeeping Mode or in any of the sensor modes, press
B
to enter the Barometer/Thermometer Mode.
• BARO will appear on the display, indicating that barometric
pressure and temperature measurements are in progress. The
measurement results will appear on the display after about fi ve
seconds.
• After you press
B
, the watch will take readings every fi ve seconds
for the fi rst fi ve minutes, and then every two minutes after that.
2. Press
D
to return to the Timekeeping Mode.
• The watch will return to the Timekeeping Mode automatically if you
do not perform any operation for about one hour after entering the
Barometer/Thermometer Mode.
To take barometric pressure and temperature readings
While in the Timekeeping Mode or in any of the sensor modes, press
B
.
• This starts barometric pressure and temperature measurements automatically.
• You also can perform a barometric pressure and temperature measurement at any time by pressing
B
in the Barometer/Thermometer Mode.
• It can take up to four or fi ve seconds for the barometric pressure reading to appear after you enter the
Barometer/Thermometer Mode.
Barometric Pressure
• Barometric pressure is displayed in units of 1 hPa (or 0.05 inHg).
•
The displayed barometric pressure value changes to
- - -
if a measured
barometric pressure falls outside the range of 260 hPa to 1,100 hPa (7.65
inHg to 32.45 inHg). The barometric pressure value will reappear as
soon as the measured barometric pressure is within the allowable range.
Temperature
• Temperature is displayed in units of 0.1°C (or 0.2°F).
• The displayed temperature value changes to
- - -
°C (or °F) if a
measured temperature falls outside the range of –10.0°C to 60.0°C
(14.0°F to 140.0°F). The temperature value will reappear as soon as
the measured temperature is within the allowable range.
Display Units
You can select either hectopascals (hPa) or inchesHg (inHg) as the display unit for the measured
barometric pressure, and Celsius (°C) or Fahrenheit (°F) as the display unit for the measured temperature
value. See “To specify temperature, barometric pressure, and altitude units”.
Barometric Pressure Graph
Barometric pressure indicates changes in the atmosphere. By monitoring
these changes you can predict the weather with reasonable accuracy.
This watch takes barometric pressure measurements automatically every
two hours (at the 30th minute of every even numbered hour).
Measurement results are used to produce barometric pressure graph and
barometric pressure differential pointer readings.
Reading the Barometric Pressure Graph
The barometric pressure graph shows readings of previous measurements for up to 24 hours.
• The horizontal axis of the graph represents time, with each dot
standing for two hours. The rightmost dot represents the most recent
reading.
• The vertical axis of the graph represents barometric pressure, with
each dot standing for the relative difference between its reading and
that of the dots next to it. Each dot represents 1 hPa.
12 o’clock
position
Bearing
memory
pointer
North
pointer
Direction angle of
current reading
Bearing memory
direction angle
value
12 o’clock
position
Bearing
memory
pointer
North
pointer
Direction angle of
current reading
Bearing memory
direction angle
value
Temperature
Barometric
pressure graph
Barometric
pressure
Pressure differential
pointer
Temperature
Barometric
pressure graph
Barometric
pressure
Pressure differential
pointer
Temperature
Barometric
pressure
Temperature
Barometric
pressure
Barometric
pressure graph
Barometric
pressure graph
Barometric
pressure
Time
Barometric
pressure
Time